Appearance
原文链接:
TIP
搬运这边文章,确实因为它解决了我对类型声明文件的一些疑惑:
- 如何定义
.d.ts文件 - 如何使用
compilerOptions#typeRoots引入自定义types,以及第三方node_modules/@types/** - 如何使用三斜线指令引入类型,以及引入
<reference />后的类型共享 - 环境声明(
ambient declarations)& 环境值 (ambient values)是什么?只允许定义,不允许实现或者值的存在 - 如何在声明文件中使用
namespace解决可能存在的命名冲突, namespace本质上是一个对象字面量,但是声明文件中是不允许存在对象的,因此需要写成declare namespce XXX {}形式,将其变为一个环境值😎 - 模块系统(使用
export {}等方式)对全局环境类型的影响🔥,如何使用declare global {}引入全局类型解决这一问题
类型声明(Type Declaration) 或者 类型定义(Type Definition) 文件是一个以.d.ts作为文件后缀名的TypeScript文件。它们与普通.ts文件有什么区别呢?有什么特征呢?接下来,一起深入了解下。
一..d.ts文件
类型声明文件的后缀名为.d.ts,文件中只包含与类型相关的代码,不包含逻辑代码,它们的作用旨在为开发者提供类型信息,所以它们只在开发阶段起作用🎉。
TIP
📚 typescript编译后会将类型信息移除,类型信息仅在开发阶段起作用。
类型声明,即类型的声明,例如interface、function和class,下面是一个interface声明。
typescript
// Person接口类型声明
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
}
// 使用Person接口
const xm: Person = {
name: 'XiaoMing',
age: 8
}二.全局声明
全局声明(global declaration) 在任何TypeScript项目或者TypeScript代码片段中都会起作用的。例如当你写下const p = new Promise();时,TypeScript编译器不会去编译你的代码,因为const p = new Promise();语法错误了,如果你使用的是vscode IDE,那么vscode向下图中那样提示你。
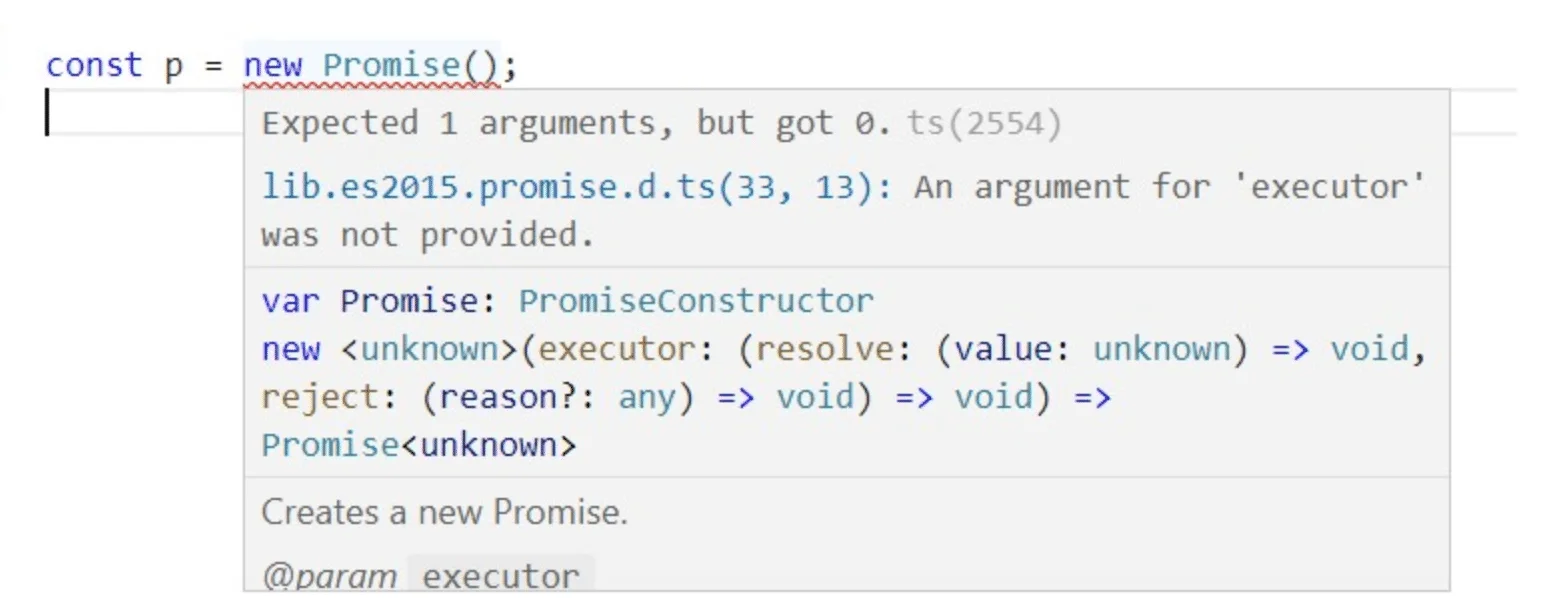
vscode就是根据全局声明检测到你的语法错误的。每个TypeScript程序都可以使用全局声明,无需显示的用import语句导入。
从IDE的提示中,可以看到Promise类型是定义在lib.es2015.promise.d.ts文件中的,由TypeScript提供,TypeScript提供的很多这样的声明文件,被称作标准库📚(这些声明文件会随TypeScript一起安装)。
TIP
使用lib编译选项,你可以控制哪些标准库被引入到当前项目。也可以设置noLib为true,这样会在项目中禁用所有标准库。
为了手动的去加载一些全局声明文件,我们需要告诉TypeScript编译器声明文件的位置。可以通过typeRoots和types编译选项设置,关于这些内容,我也在tsconfig overview里面讲解过。
接下来,动手实践。创建以下文件结构:
bash
.
├── program.ts
├── tsconfig.json
└── types
└── common
├── main.d.ts
└── package.json在我们的项目中,我们需要一些公共类型,在每个ts文件中都可以使用这些公共类型,所以我打算在project/types/common/main.d.ts中存放这些公共类型声明,使用typeRoots告诉TypeScript声明文件的位置。TypeScript编译器会根据Node模块定位策略导入typeRoots指定的目录下的声明文件,如果没有提供typeRoots选项,默认会导入node_modules/@types文件夹中的声明文件。
node_modules/@types是typeRoots的默认值,node_modules/@types的目的仅仅是为了提供公共包的类型声明,目录下的每个声明模块的根目录下都应该包含一个index.d.ts文件,用来作为typescirpt入口声明文件,如果没有index.d.ts文件,它应该有一个package.json文件,package.json文件需要指出入口声明文件的位置。
现在我需要把project/types/common/main.d.ts文件,作为入口声明文件,所以在project/types/common/package.json文件中需要添加以下内容。
json
{
"name": "common",
"version": "1.0.0",
// "typings" 或者 "types" 都可以
"typings": "main.d.ts"
}typings用于指示入口声明文件的位置。
接下来,配置typeRoots,告诉TypeScript自定义全局声明的位置,修改tsconfig.json文件内容如下。
json
{
"files": [
"./program.ts"
],
"compilerOptions": {
"typeRoots": [
"./types"
]
}
}在main.d.ts文件中添加声明信息。
typescript
interface Person {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
age: number;
}有了声明信息,可以在program.ts中使用该类型了。
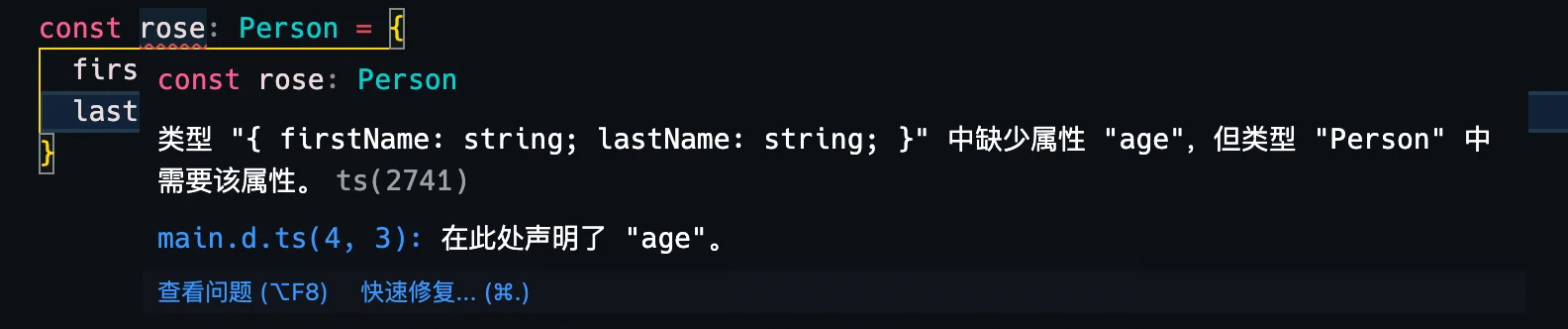
正如图片中显示的那样,定义了Person类型的ross变量,因为赋值与类型不兼容,所以IDE报错,IDE还给出了声明文件的位置。修改program.ts文件如下,修复错误。
typescript
const ross: Person = {
firstName: "Ross",
lastName: "Geller",
age: 20
};三.声明模块化
在上面的例子中,TypeScript仅仅知道main.d.ts声明文件,假如项目中包含几千个声明信息,将这些声明全部放到main.d.ts文件中,会使项目变得非常糟糕,不好维护。因此,需要将声明模块化。
在命名空间教程中,我介绍过可以使用 <reference />指令,在编译阶段添加一些文件。当然我们也可以在声明文件中使用该指令。首先project/types/common/文件夹下添加functions.d.ts和interfaces.d.ts文件。
interfaces.d.ts提供common包中所有的接口类型信息,functions.d.ts提供common包中所有的函数类型信息。并在main.d.ts文件中,使用<reference />指令引入它们。
typescript
/// <reference path="./interfaces.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="./functions.d.ts" />typescript
interface Person {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
age: number;
}typescript
type GetFullName = ( p: Person ) => string;有一点值得注意的是,我们可以在functions.d.ts文件中,使用interfaces.d.ts文件中定义的Person接口,这是因为使用<reference />指定,指定的文件可以共享类型声明😎。
修改program.ts文件使用定义的类型。
typescript
const ross: Person = {
firstName: "Ross",
lastName: "Geller",
age: 20
};
const getPersonName: GetFullName = (p: Person) => {
return `${p.firstName} ${p.lastName}`;
};
console.log(getPersonName(ross));四.第三方声明
目前,已经知道了如何创建自定义全局声明文件。某些情况下,我们需要安装第三方提供的npm声明文件包。
在Compilation文章中我提到过DefinitelyTyped社区,它们为我们提供了很多第三方npm声明文件包,例如@types/lodash和@types/node等等。你可以使用npm安装@types下的声明包。
bash
npm install -D @types/node这些包会被下载到node_modules/@types文件夹下,这也是为什么typeRoots的默认值为node_modules/@types。如果你想在默认值的基础上额外添加一个声明文件夹目录,需要给typeRoots指定两个值。
json
{
"files": [
"./program.ts"
],
"compilerOptions": {
"typeRoots": [
"./node_modules/@types",
"./types"
]
}
}五.环境相关的声明
某些值,只存在于运行时。例如window对象,它只存在于浏览器环境中,同样的还有node中的global。
如果当你在TypeScript程序中,使用window或者glbal时,typescirpt编译器报错了cannot find name 'window'。这是正常的,因为没有定义window变量。所以,如果没有定义,我们如何使用window对象呢?
我们需要使用declare关键字告诉TypeScript编译器,window变量存在,不要再报错了。
typescript
declare var window: any;这句代码,被称为环境声明(ambient declaration),其中window被称为环境值(ambient value)。有了这个声明,TypeScript会认为这个any类型的window变量已经定义了,所以在任何地方使用window变量都不会报错了。
你也可以为环境值提供指定的类型,例如declare var window: Person;
接下来,在main.d.ts文件中添加一个环境值XiaoMing。
typescript
/// <reference path="functions.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="interfaces.d.ts" />
// 只有定义 没有实现,称之为 环境声明(ambient declaration)
// XiaoMing 则表示是环境值(ambient value)
declare var XiaoMing: Person 然后在program.ts中使用它。
typescript
console.log(XiaoMing.age);如果没有写错的话,TypeScript不会报错。
六.命名空间的声明
在前面的例子中,我们提供了types/common声明包,定义了全局Person接口类型,全局的接口类型有一个弊端,就是很容易被其他包里的声明文件类型覆盖(类型冲突)。
为了避免这个问题,最好的解决方式是将类型定义在命名空间里。在namespace文章中,介绍了namespace的用法,我们可以在命名空间里定义类型声明。
修改声明文件内容如下。
typescript
// 使用namespcae
declare namespace common {
interface Person {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
age: number;
}
}typescript
declare namespace common {
type GetFullName = ( p: Person ) => string;
}typescript
/// <reference path="./interfaces.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="./functions.d.ts" />这里定义的命名空间类型与namespace文章中有点不一样,区别在于使用了declare关键字。因为namespace是一个值(object),在声明文件.d.ts文件中应该将namespace定义成环境值,这样我们可以在任何ts文件中,通过common命名空间使用common.<type>类型,例如common.Person。
WARNING
🚨再次提醒,在声明文件中只允许包含声明信息,因为命名空间是一个object,所以不能在声明文件中定义它,但是我们可以将命名空间定义成环境值。
并且,当命名空间被定义在声明文件中,export关键字就不需要了,命名空间内部的所有类型,都被隐式export。另外,你不能从命名空间中导出一个值,只允许导出类型。
七.类型扩展
当typescript预见多个同名接口类型,它会自动合并这些接口类型成为一个声明。
namespace也有类似的行为,当声明一个已经存在的命名空间时,typescript会自动扩展已经存在的命名空间。所以当接口和命名空间在全局环境中,可以重新声明它们来达到扩展它们的目的。
更新声明文件。
typescript
// Person 不使用 namespcae
interface Person {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
age: number;
}typescript
declare namespace common {
type GetFullName = ( p: Person ) => string;
}typescript
/// <reference path="./interfaces.d.ts" />
/// <reference path="./functions.d.ts" />更新program.ts。
typescript
// 与types/common/interfaces.d.ts中的Person interface合并
interface Person {
email: string;
}
// 扩展原生的Number类型
interface Number {
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/44481256/7185283
isEven: () => boolean;
}
const ross: Person = {
firstName: "Ross",
lastName: "Geller",
age: 29,
email: "ross@geller.com"
};
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/32330345/7185283
Number.prototype.isEven = function(this: number): boolean {
return this % 2 === 0
}
const isAgeEven = ross.age.isEven();
console.log("isAgeEven", isAgeEven);此时typescript并不会报错。在program.ts中扩展了Person接口和Number(内置类型)接口。
但是,这并不适用于模块系统(CJS | ESM等),值和类型只能在script文件中共享,script文件就是不包含import和export语句的文件。
可以在program.ts文件最后面添加一行代码export {}。
typescript
// 与types/common/interfaces.d.ts中的Person interface合并
interface Person {
email: string;
}
// 扩展原生的Number类型
interface Number {
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/44481256/7185283
isEven: () => boolean;
}
const ross: Person = {
firstName: "Ross",
lastName: "Geller",
age: 29,
email: "ross@geller.com"
};
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/32330345/7185283
Number.prototype.isEven = function(this: number): boolean {
return this % 2 === 0
}
const isAgeEven = ross.age.isEven();
console.log("isAgeEven", isAgeEven);
// 🚀引入下面语句,将 program.ts文件变为了一个模块,而不是全局的script
export {} 此时typescript应该会给出以下错误信息。
bash
Type '{ firstName: string; lastName: string; age: number; email: string; }' is not assignable to type 'Person'.
Object literal may only specify known properties, and 'firstName' does not exist in type 'Person'.ts(2322)
Property 'age' does not exist on type 'Person'.ts(2339)因为,添加export {}代码,将program.ts文件转换成了模块(module),这种情况下,typescript不会扩展全局环境中的类型,而是在当前模块内重新声明该类型。
那么如何在模块中,扩展全局环境中的类型呢?TypeScript提供了declare global环境声明语句,使用它,可以在模块内给全局作用域添加声明。
更新program.ts,使用declare global语句。
typescript
declare global {
interface Person {
email: string;
}
}
declare global {
interface Number {
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/44481256/7185283
isEven: () => boolean;
}
var Version: string
}
const rose: Person = {
first: 'rose',
last: 'durant',
age: 36,
email: 'rose@example.com'
}
const getFullname: common.GetFullname = (p: Person) => {
return p.first + ' ' + p.last
}
// var version = 20
console.log(getFullname(rose))
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/32330345/7185283
Number.prototype.isEven = function(this: number): boolean {
return this % 2 === 0
}
console.log(rose.age.isEven())
// console.log(XiaoMing.age)
// var version: Version = '1.0.0'
const Version = '1.0.0'
console.log(Version)
export {}这次typescript不会报错,并且成功在module内扩展了全局类型😎。
2023年02月26日00:18:37